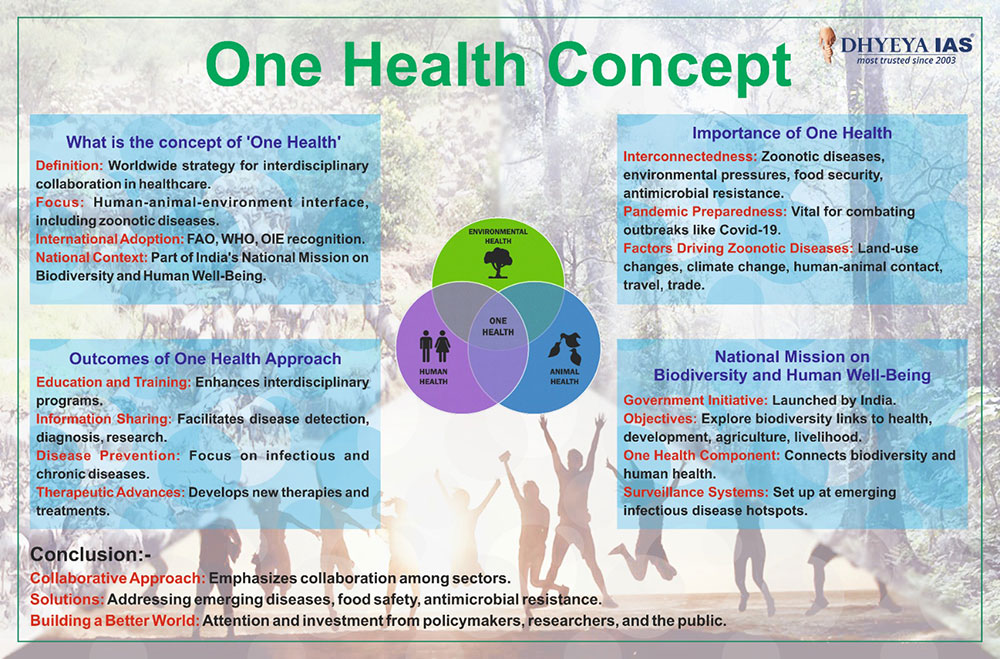
Info-paedia : One Health Concept
What is the concept of ‘One Health’
- Definition: Worldwide strategy for interdisciplinary
collaboration in healthcare.
- Focus: Human-animal-environment interface, including zoonotic
diseases.
- International Adoption: FAO, WHO, OIE recognition.
- National Context: Part of India's National Mission on
Biodiversity and Human Well-Being.
Importance of One Health
- Interconnectedness: Zoonotic diseases, environmental pressures,
food security, antimicrobial resistance.
- Pandemic Preparedness: Vital for combating outbreaks like
Covid-19.
- Factors Driving Zoonotic Diseases: Land-use changes, climate
change, human-animal contact, travel, trade.
Outcomes of One Health Approach
- Education and Training: Enhances interdisciplinary programs.
- Information Sharing: Facilitates disease detection, diagnosis,
research.
- Disease Prevention: Focus on infectious and chronic diseases.
- Therapeutic Advances: Develops new therapies and treatments.
National Mission on Biodiversity and Human Well-Being
- Government Initiative: Launched by India.
- Objectives: Explore biodiversity links to health, development,
agriculture, livelihood.
- One Health Component: Connects biodiversity and human health.
- Surveillance Systems: Set up at emerging infectious disease
hotspots.
Conclusion
- Collaborative Approach: Emphasizes collaboration among sectors.
- Solutions: Addressing emerging diseases, food safety,
antimicrobial resistance.
- Building a Better World: Attention and investment from
policymakers, researchers, and the public.